Heart disease: Disease that affect the heart and cardiovascular system
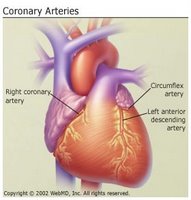
When you think of heart disease, usually people think of coronary artery disease (narrowing of the arteries leading to the heart), but coronary artery disease is just one type of cardiovascular disease.
Cardiovascular disease includes a number of conditions affecting the structures or function of the heart. They can include:
* Coronary artery disease (including heart attack)
* Abnormal heart rhythms or arrythmias
* Heart failure
* Heart valve disease
* Congenital heart disease
* Heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy)
* Pericardial disease
* Aorta disease and Marfan syndrome
* Vascular disease (blood vessel disease)
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women in the U.S. It is important to learn about your heart to help prevent heart disease. And, if you have cardiovascular disease, you can live a healthier, more active life by learning about your disease and treatments and by becoming an active participant in your care.
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is atherosclerosis, or hardening, of the arteries that provide vital oxygen and nutrients to the heart.
Abnormal Heart Rhythms
The heart is an amazing organ. It beats in a steady, even rhythm, about 60 to 100 times each minute (that's about 100,000 times each day!). But, sometimes your heart gets out of rhythm. An irregular or abnormal heartbeat is called an arrhythmia. An arrhythmia (also called a dysrhythmia) can involve a change in the rhythm, producing an uneven heartbeat, or a change in the rate, causing a very slow or very fast heartbeat.
Heart Failure
The term "heart failure" can be frightening. It does not mean the heart has "failed" or stopped working. It means the heart does not pump as well as it should.
Heart failure is a major health problem in the U.S., affecting nearly 5 million Americans. About 550,000 people are diagnosed with heart failure each year. It is the leading cause of hospitalization in people older than 65.
Heart Valve Disease
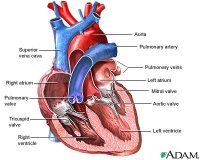
Your heart valves lie at the exit of each of your four heart chambers and maintain one-way blood-flow through your heart.
Examples include mitral valve prolapse, aortic stenosis and mitral valve insufficiency.
Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital heart disease is a type of defect in one or more structures of the heart or blood vessels that occur before birth.
It affects about 8 out of every 1,000 children. Congenital heart defects may produce symptoms at birth, during childhood and sometimes not until adulthood.
In most cases scientists don't know why they occur. Heredity may play a role as well as exposure to the fetus during pregnancy to certain viral infections, alcohol or drugs.
Cardiomyopathies
Cardiomyopathies are diseases of the heart muscle itself. People with cardiomyopathies have hearts that are abnormally enlarged, thickened and/or stiffened. As a result, the heart's ability to pump blood is weakened. Without treatment, cardiomyopathies worsen over time and often lead to heart failure and abnormal heart rhythms.
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is inflammation of the lining that surrounds the heart. It is a rare condition often caused by an infection.
Aorta Disease and Marfan syndrome
The aorta is the large artery that leaves the heart and provides oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. These diseases and conditions can cause the aorta to dilate (widen) or dissect (tear), increasing the risk for future life-threatening events:
* Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
* Hypertension (high blood pressure).
* Genetic conditions such as Marfan Syndrome.
* Connective tissue disorders (that affect the strength of the blood vessel walls) such as, scleroderma, osteogenesis imperfecta, polycystic kidney disease and Turner's syndrome.
* Injury.
People with aorta disease should be treated by an experienced team of cardiovascular specialists and surgeons.(source:www.webmd.com)


0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home